ucontext-人人都可以实现的简单协程库 github地址 vscode c++调试环境搭建 程序员应如何理解协程
在此记录一下协程的基本概念,后续再考虑实现手写的协程。
uthread说明
一个简单的C++用户级线程(协程)库
一个调度器可以拥有多个协程
通过uthread_create创建一个协程
通过uthread_resume运行或者恢复运行一个协程
通过uthread_yield挂起一个协程,并切换到主进程中
通过schedule_finished 判断调度器中的协程是否全部运行完毕
每个协程最多拥有128Kb的栈,增大栈空间需要修改源码的宏DEFAULT_STACK_SIZE ,并重新编译
更详细的介绍,请查看博客 人既无名的专栏 .
细节
ctx保存协程的上下文,stack为协程的栈,栈大小默认为DEFAULT_STACK_SZIE=128Kb.你可以根据自己的需求更改栈的大小。
func为协程执行的用户函数,arg为func的参数
state表示协程的运行状态,包括FREE,RUNNABLE,RUNING,SUSPEND,分别表示空闲,就绪,正在执行和挂起四种状态。
调度器包括主函数的上下文main,包含当前调度器拥有的所有协程的vector类型的threads,以及指向当前正在执行的协程的编号running_thread.如果当前没有正在执行的协程时,running_thread=-1.
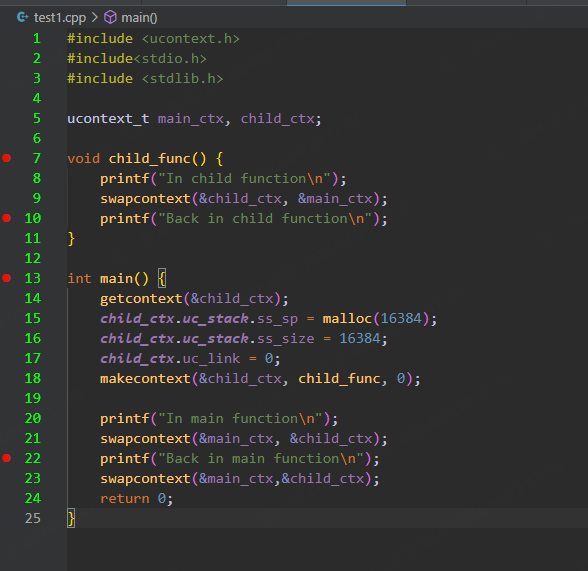
下面给出一个简单例子,可以自己打断点调试一下,
下面也给出调试的配置launch.json
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 { "version" : "0.2.0" , "configurations" : [ { "name" : "(gdb) 启动" , "type" : "cppdbg" , "request" : "launch" , "program" : "${workspaceFolder}/test1" , "args" : [ ] , "stopAtEntry" : false , "cwd" : "${fileDirname}" , "environment" : [ ] , "externalConsole" : false , "MIMode" : "gdb" , "setupCommands" : [ { "description" : "为 gdb 启用整齐打印" , "text" : "-enable-pretty-printing" , "ignoreFailures" : true } , { "description" : "将反汇编风格设置为 Intel" , "text" : "-gdb-set disassembly-flavor intel" , "ignoreFailures" : true } ] } ] }
重点是这一行 "program": "${workspaceFolder}/test1"
uthread代码
总共就只有四个文件,这里都给出来,加了一点自己的注释理解
Makefile
1 2 3 4 5 6 all: g++ uthread.cpp -g -c g++ main.cpp -g -o main uthread.o clean: rm -f uthread.o main
uthread.h
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 #ifndef MY_UTHREAD_H #define MY_UTHREAD_H #ifdef __APPLE__ #define _XOPEN_SOURCE #endif #include <ucontext.h> #include <vector> #define DEFAULT_STACK_SZIE (1024*128) #define MAX_UTHREAD_SIZE 1024 enum ThreadState {FREE,RUNNABLE,RUNNING,SUSPEND};struct schedule_t ;typedef void (*Fun) (void *arg) typedef struct uthread_t { ucontext_t ctx; Fun func; void *arg; enum ThreadState state; char stack[DEFAULT_STACK_SZIE]; }uthread_t ; typedef struct schedule_t { ucontext_t main; int running_thread; uthread_t *threads; int max_index; schedule_t ():running_thread (-1 ), max_index (0 ) { threads = new uthread_t [MAX_UTHREAD_SIZE]; for (int i = 0 ; i < MAX_UTHREAD_SIZE; i++) { threads[i].state = FREE; } } ~schedule_t () { delete [] threads; } }schedule_t ; static void uthread_body (schedule_t *ps) int uthread_create (schedule_t &schedule,Fun func,void *arg) void uthread_yield (schedule_t &schedule) void uthread_resume (schedule_t &schedule,int id) int schedule_finished (const schedule_t &schedule) #endif
uthread.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 #ifndef MY_UTHREAD_CPP #define MY_UTHREAD_CPP #include "uthread.h" void uthread_resume (schedule_t &schedule , int id) if (id < 0 || id >= schedule.max_index){ return ; } uthread_t *t = &(schedule.threads[id]); if (t->state == SUSPEND) { swapcontext (&(schedule.main),&(t->ctx)); } } void uthread_yield (schedule_t &schedule) if (schedule.running_thread != -1 ){ uthread_t *t = &(schedule.threads[schedule.running_thread]); t->state = SUSPEND; schedule.running_thread = -1 ; swapcontext (&(t->ctx),&(schedule.main)); } } void uthread_body (schedule_t *ps) int id = ps->running_thread; if (id != -1 ){ uthread_t *t = &(ps->threads[id]); t->func (t->arg); t->state = FREE; ps->running_thread = -1 ; } } int uthread_create (schedule_t &schedule,Fun func,void *arg) int id = 0 ; for (id = 0 ; id < schedule.max_index; ++id ){ if (schedule.threads[id].state == FREE){ break ; } } if (id == schedule.max_index) { schedule.max_index++; } uthread_t *t = &(schedule.threads[id]); t->state = RUNNABLE; t->func = func; t->arg = arg; getcontext (&(t->ctx)); t->ctx.uc_stack.ss_sp = t->stack; t->ctx.uc_stack.ss_size = DEFAULT_STACK_SZIE; t->ctx.uc_stack.ss_flags = 0 ; t->ctx.uc_link = &(schedule.main); schedule.running_thread = id; makecontext (&(t->ctx),(void (*)(void ))(uthread_body),1 ,&schedule); swapcontext (&(schedule.main), &(t->ctx)); return id; } int schedule_finished (const schedule_t &schedule) if (schedule.running_thread != -1 ){ return 0 ; }else { for (int i = 0 ; i < schedule.max_index; ++i){ if (schedule.threads[i].state != FREE){ return 0 ; } } } return 1 ; } #endif
main.cpp
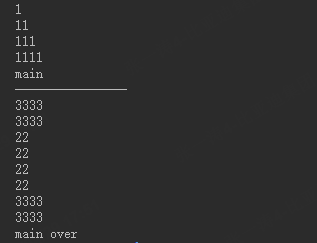
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 #include "uthread.h" #include <stdio.h> void func1 (void * arg) puts ("1" ); puts ("11" ); puts ("111" ); puts ("1111" ); } void func2 (void * arg) puts ("22" ); puts ("22" ); uthread_yield (*(schedule_t *)arg); puts ("22" ); puts ("22" ); } void func3 (void *arg) puts ("3333" ); puts ("3333" ); uthread_yield (*(schedule_t *)arg); puts ("3333" ); puts ("3333" ); } void context_test () char stack[1024 *128 ]; ucontext_t uc1,ucmain; getcontext (&uc1); uc1.uc_stack.ss_sp = stack; uc1.uc_stack.ss_size = 1024 *128 ; uc1.uc_stack.ss_flags = 0 ; uc1.uc_link = &ucmain; makecontext (&uc1,(void (*)(void ))func1,0 ); swapcontext (&ucmain,&uc1); puts ("main" ); } void schedule_test () schedule_t s; int id1 = uthread_create (s,func3,&s); int id2 = uthread_create (s,func2,&s); while (!schedule_finished (s)){ uthread_resume (s,id2); uthread_resume (s,id1); } puts ("main over" ); } int main () context_test (); puts ("----------------" ); schedule_test (); return 0 ; }
输出如下所示