TinyAgent
关键代码
1 | def text_completion(self, text, history=[]): |
总结:
- 首先对输入文本加一个"question"前缀,然后送入
model得到response、his self.system_prompt就是事先人为构造好的prompt格式- 然后再从
response里面拿到plugin_name,plugin_args,response;如果有plugin_name就调用插件(tool)将结果拼接到response末尾 - 最后再送入model拿到结果
TinyRAG
datawhale这块程序写的有一点问题,就总结一下大概思路吧
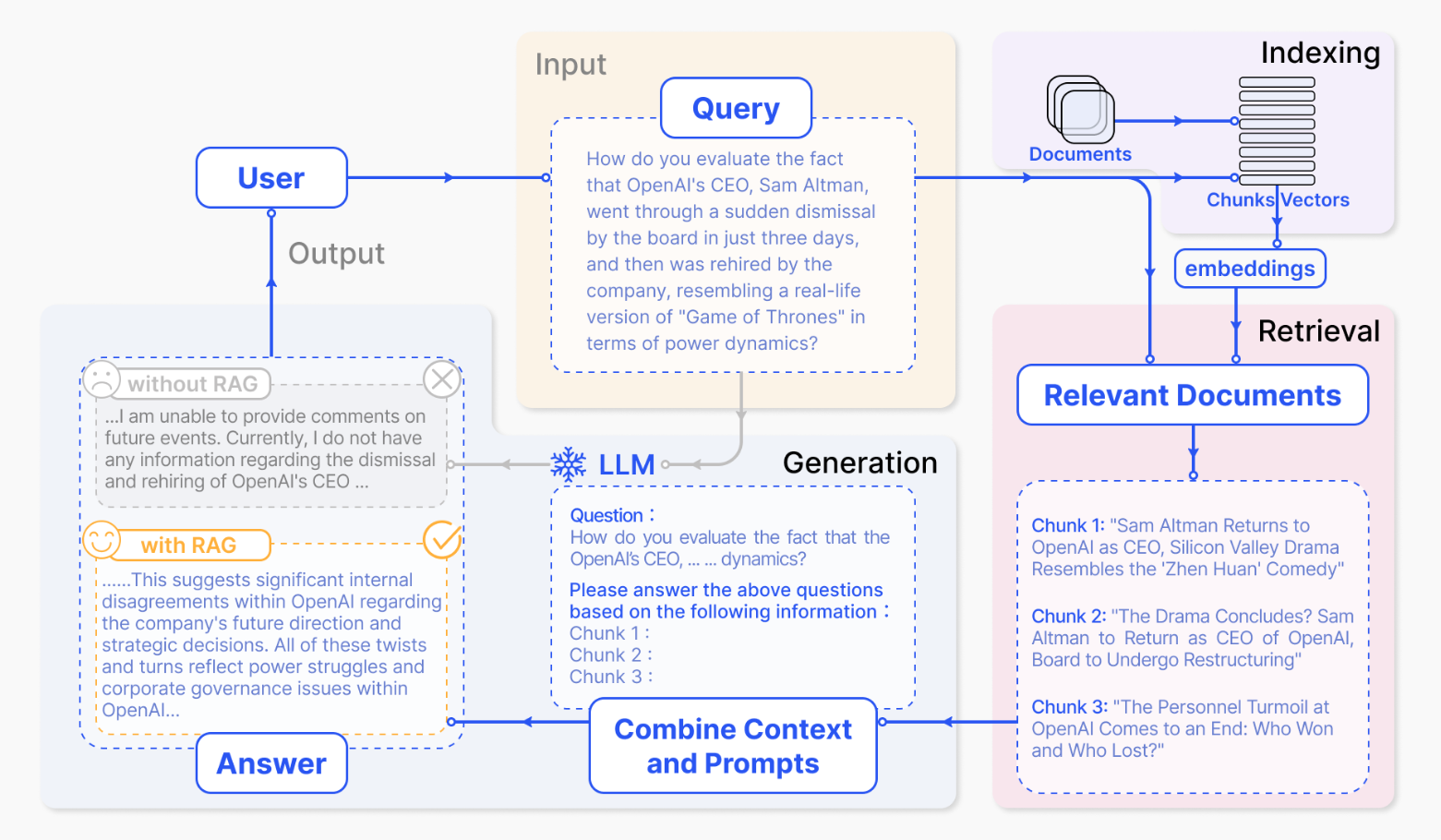 具体操作细节可以看官网文档的readme.md
具体操作细节可以看官网文档的readme.md
RAG的五个部分
- 向量化模块
- 文档加载和切分模块
- 数据库
- 向量检索
- 大模型模块
一般来说,RAG具体流程可以总结如下:
- 将输入文本
text经过embedding后转vectors存着 - 同样的将
query经过类似操作得到vector,然后计算第一步得到的vectors之间的余弦相似度,返回k个最接近的 - 再输入给
LLM得到结果
感觉主要问题就在embedding和retrieval这两部分,前者貌似一般都有开源的embbeding model,顶多再微调一下,而后者着重向量的构建,检索速度的优化?
2024/8/13更新
后面有空再去看一下有道QAnything,感觉是一个不错的RAG实践。